Castling Chess – Ultimate Guide In 2024!
In the intricate world of chess strategy, castling stands as a cornerstone maneuver, blending defensive fortification with strategic maneuvering.
Castling in chess is a strategic move where the king and one rook are moved simultaneously to enhance safety and activate pieces.
Understanding the nuances of castling is pivotal for players at every skill level, as it shapes the flow and outcome of the game in profound ways. Let’s explore.
Introduction To Castling Chess:
Castling in chess is a special move where the king and one of the rooks move simultaneously. The king moves two squares towards a rook, and the rook moves to the square next to the king.
It’s the only move in chess where two pieces can be moved in one turn. Castling is primarily used for king safety and rook activation.
It’s subject to specific conditions, including the king not being in check and no pieces obstructing the path.
Understanding The Rules Of Castling:
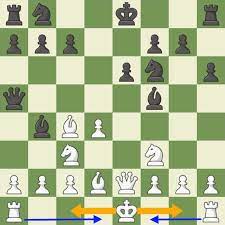
In chess, casting is a special move involving the king and one of the rooks. It’s the only move where the king can move two squares toward a rook, and that rook then jumps over the king to land on the square next to it.
However, some conditions must be met for castling to be allowed:
- Both the king and the rook involved in castling can have moved previously.
- There should be no pieces between the king and the rook.
- The king cannot be in check.
- The squares the king crosses and the squares it ends on cannot be under attack by any of the opponent’s pieces.
Benefits Of Castling:
1. King Safety:
Castling is crucial for protecting the king. By moving it to a corner and shielding it with pawns, castling creates a stronghold that’s hard to breach, keeping the king safe from threats.
2. Rook Activation:
Castling activates one of the rooks, freeing it from the corner. This allows the rook to control open lines and contribute more effectively to the game’s dynamics.
3. Centralization:
Castling often involves bringing the king closer to the center. This grants greater control over critical squares and facilitates defensive and offensive maneuvers.
4. Connectivity:
Castling improves the coordination between the king and rook. By positioning them closer, castling enhances their ability to support each other and coordinate strategic plans.
5. Initiating Endgame:
Castling can signal the transition to the endgame phase. As players complete their development, castling helps consolidate their position and prepares them for the game’s final stage.
Common Mistakes In Castling:
1. Ignoring Safety Measures:
One of the most common mistakes is prioritizing castling without ensuring the king’s safety. Players may need to pay more attention to potential threats or adequately protect the squares around the king, leaving it vulnerable to attacks.
2. Timing Issues:
Another mistake is improper timing of castling. Players may castle too early, before completing their development or adequately preparing their position, which can expose them to tactical vulnerabilities.
On the other hand, delaying castling for too long can result in missed opportunities to improve king safety and activate rooks.
3. Overlooking Opponent’s Position:
Players often need to consider their opponent’s position before castling. Failing to assess the opponent’s threats, potential attacks, or tactical possibilities can lead to disastrous consequences, such as falling into traps or allowing the opponent to gain a significant advantage.
Advanced Castling Techniques:
1. Queen Side Castling:
This technique involves moving the king two squares towards the queenside rook and placing the rook next to the king.
It can surprise opponents and create unique positional dynamics, particularly in closed or symmetrical pawn structures.
2. Castling In Complex Positions:
Knowing when to castle in complex positions requires deep understanding and calculation skills. Players must evaluate risks and benefits based on pawn structure and piece activity.
3. Delayed Castling:
Delaying castling maintains flexibility and keeps opponents guessing. It can also force opponents to reveal their plans first or create tension in the center before committing to a specific side.
4. Castling Into Attack:
Castling can be part of an aggressive strategy, especially when the opponent’s king is in the center.
By castling into attack, players can quickly mobilize pieces and launch assaults while leveraging the safety of their king.
5. Castling As A Defensive Resource:
Castling remains crucial for defense, providing sanctuary for the king amidst tactical chaos. It allows players to fortify their position against threats and regroup for counterattacks.
The Evolution Of Castling In Chess History
Throughout history, the rules and significance of castling have evolved. From medieval chess to modern competitive play, castling has undergone refinements and adaptations.
Famous Castling Maneuvers In Grandmaster Games
Many memorable games feature brilliant casting maneuvers that demonstrate the strategic depth of chess. Studying these games can inspire and educate players about the power of castling.
Castling In Chess Strategy:
Castling plays a central role in chess strategy, offering both positional and tactical advantages:
- Positional Advantage: Castling contributes to the harmonious development of pieces and solidifies the player’s position.
- Tactical Opportunities: Castling can create threats and tactical possibilities, especially when combined with other strategic elements.
Castling Variations In Different Chess Formats:
Various chess formats, such as blitz, rapid, and correspondence chess, have different dynamics that influence castling strategies. Understanding these variations is essential for adapting one’s play style accordingly.
Teaching Castling To Beginners:
For novice players, learning to castle effectively is a crucial step in their chess education. Simplifying the rules and emphasizing the benefits of castling can help beginners grasp this concept more easily.
Practicing Castling: Tips And Exercises:
Practicing castling in different scenarios can improve one’s skills and decision-making:
- Setting up specific positions to practice castling under various conditions.
- Analyzing games to identify opportunities for castling and evaluate its effectiveness.
Psychological Impact Of Castling:
Castling can have psychological effects on both players. It can instill confidence and security in the player executing it while prompting the opponent to reassess their strategy and tactics.
The Future Of Castling In Chess:
As chess continues to evolve with advancements in technology and new generations of players, the role of castling may undergo further scrutiny and adaptation. However, its fundamental importance in chess strategy is likely to endure.
Conclusion:
Castling is more than just a defensive maneuver in chess; it’s a strategic tool that shapes the dynamics of the game. Understanding when and how to castle is essential for players aiming to improve their skills and master the complexities of chess.
FAQs:
1. Is Castling Mandatory In Chess?
No, castling is not mandatory. It’s a strategic option available to players but not a requirement.
2. Can I Castle If My King Or Rook Has Moved Previously?
No, neither the king nor the rook involved in castling can have moved previously for castling to be permissible.
3. Can I Castle Out Of Check?
No, castling is not allowed if the king is in check or would pass through a square that is under attack.
4. What Is The Purpose Of Castling?
Castling serves the dual purpose of safeguarding the king while activating one of the rooks, enhancing the player’s position and defensive capabilities.
5. Can I Castle With Pieces Between My King And Rook?
No, castling requires clear squares between the king and the rook involved; otherwise, it’s not permissible.
Read More:






