What Is Gpu Hotspot Temperature? – A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered why your computer’s GPU gets so hot during intense gaming sessions or video editing tasks? The answer lies in the elusive concept of GPU hotspot temperature.
The GPU hotspot temperature is the highest temperature measured at a specific location on the graphics processing unit (GPU) die, indicating the hottest point on the chip.
Join us as we unravel the mysteries behind GPU hotspot temperature and discover how it plays a crucial role in high-performance computing.
Understanding Gpu Hotspot Temperature:
The GPU hotspot temperature is recorded at the hottest point within the GPU die. Unlike the average GPU temperature, which considers all sensors collectively, the hotspot temperature explicitly identifies the end of maximum heat.
This metric is crucial for assessing the risk of overheating and ensuring the overall health and performance of the GPU. It is crucial to monitor and control the GPU hotspot temperature to prevent thermal issues, optimize performance, and prolong hardware lifespan.
The temperature of the GPU hotspot can vary depending on factors like workload, ambient temperature, and cooling efficiency. Utilizing software tools to track this metric is essential for ensuring GPUs operate within safe limits.
Effectively understanding and managing the GPU hotspot temperature can result in improved performance, increased hardware longevity, and a decreased likelihood of overheating-related problems.
Unveiling The Importance Of GPU Hotspot Temperature In Optimizing Performance And Reliability:

1. Detection Of Maximum Heat:
The GPU hotspot temperature signifies the highest recorded temperature among the sensors embedded within the GPU die. It identifies specific locations on the GPU that experience the highest temperatures during operation.
2. Risk Of Excessive Heat:
Monitoring the hotspot temperature is vital to identify and address the risk of overheating. If not managed correctly, elevated temperatures can lead to performance problems, system instability, and potentially permanent damage to the GPU.
3. Thermal Strain On Components:
Overheating can subject the GPU components, especially the silicon structures, to thermal strain. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures may contribute to the deterioration of the GPU over time, affecting its overall lifespan.
4. Safe Operating Thresholds:
There are recommended temperature thresholds to prevent damage to the GPU. Surpassing these limits, particularly temperatures above 125℃, can permanently damage the GPU.
5. Effective Cooling Management:
Comprehending the hotspot temperature is vital for enhancing cooling solutions. Efficient cooling systems, including fans, heatsinks, and liquid cooling solutions, assist in maintaining the hotspot temperature within safe ranges.
6. Performance Adjustment:
GPUs are designed to adjust their performance when temperatures reach critical levels automatically. This adjustment serves as a protective mechanism to prevent the GPU from operating under potentially harmful conditions.
7. Impact Of Overclocking:
Enthusiast users who overclock their GPUs should pay close attention to the hotspot temperature. Overclocking increases the workload and heat generation, making it essential to manage temperatures effectively.
8. Precision In Temperature Monitoring:
The hotspot temperature provides a more specific and localized heat indicator than the average GPU temperature. It enables users to identify areas within the GPU die that may require additional cooling or attention.
9. Long-Term GPU Well-Being:
Maintaining the GPU hotspot temperature within safe limits contributes to the long-term well-being and reliability of the graphics card. Regular monitoring and maintenance help ensure consistent performance over the GPU’s lifespan.
10. User Awareness And Control:
Awareness of the GPU hotspot temperature empowers users to make informed decisions about system configurations, cooling solutions, and overclocking settings. Users can take preventive measures to avoid potential issues associated with overheating.
A Step-By-Step Guide On How To Monitor GPU Hotspot Temperature For Enhanced Performance:
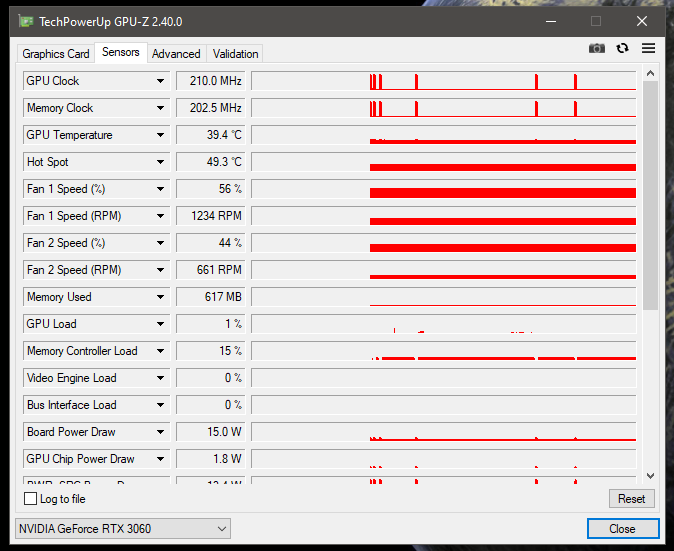
Here are steps on how to monitor GPU hotspot temperature:
1. Employ Monitoring Software:
- Utilize specialized monitoring applications designed to furnish real-time details regarding GPU temperatures.
- Well-known tools include HWiNFO, HWMonitor, GPU-Z, MSI Afterburner, and CAM.
2. Download And Install The Software:
- Retrieve the chosen monitoring software from the official website or a reliable source.
- Install the software on your computer by adhering to the provided instructions.
3. Initiate Monitoring Software:
- Launch the installed monitoring software on your computer.
4. Navigate To GPU Temperature Section:
- Locate the section or tab that exhibits GPU-related information within the monitoring software interface.
- Look for temperature data encompassing GPU temperature, hotspot temperature, and VRAM temperature.
5. Identify Gpu Hotspot Temperature:
- Specifically, seek out the GPU hotspot temperature reading within the software interface.
- The hotspot temperature represents the highest temperature recorded among the various sensors on the GPU die.
6. Observe Real-Time Changes:
- Monitor temperature readings in real time as your GPU handles diverse workloads.
- Be vigilant for noteworthy temperature spikes or fluctuations.
7. Record And Analyze Data:
- Some monitoring tools enable you to document temperature data over time.
- Analyze the recorded data to discern patterns, peak temperatures, and potential areas for enhancing cooling.
8. Set Up Alerts (If Desired):
- Specific monitoring applications permit the configuration of temperature alerts.
- Set up alerts to receive notifications when GPU temperature or hotspot temperature surpasses predefined thresholds.
9. Check Manufacturer’s Software:
- Graphics card manufacturers often supply their monitoring software.
- Verify if your GPU manufacturer offers software with specific temperature monitoring and control features.
10. Integrate Monitoring Into Game Overlays:
- Some monitoring applications allow overlaying temperature information on your game screen. This provides real-time visibility without the need to switch between applications.
11. Utilize Bios/UEFI Settings (Advanced Users):
- Proficient users may locate GPU temperature information in the computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings. Access the BIOS/UEFI during system startup to examine temperature-related data.
12. Consider External Temperature Sensors (Advanced Users):
- Advanced users can explore external temperature sensors that provide additional monitoring capabilities.
- Strategically place these sensors to measure ambient temperatures or specific components.
Understanding The Consequences Of Elevated GPU Hotspot Temperature On Performance And Hardware Longevity:
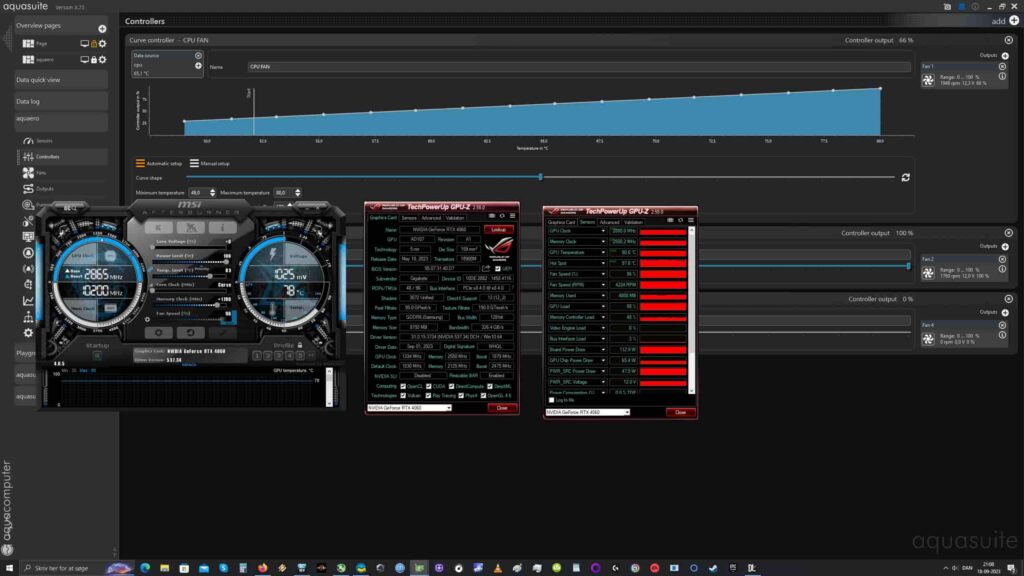
Here are the potential effects of sustained high GPU hotspot temperatures:
1. Diminished Performance:
Elevated temperatures can trigger thermal throttling, wherein the GPU automatically reduces its clock speeds to mitigate heat. Throttling leads to a decline in performance, resulting in frame rate fluctuations and disruptions in games or other GPU-intensive activities.
2. Component Deterioration:
Extended exposure to high temperatures can expedite the deterioration of the GPU’s internal components, including the silicon die. Over time, this can impact the overall longevity and dependability of the graphics card.
3. Escalated Wear And Tear:
Heightened temperatures increase wear and tear on the GPU and its adjacent components. Continually expanding and contracting materials due to temperature fluctuations can induce fatigue, potentially leading to hardware malfunctions.
4. Risk Of Thermal Throttling:
Thermal throttling serves as a protective mechanism employed by GPUs to prevent overheating. If the hotspot temperature surpasses safe limits, the GPU may throttle its performance to cool down, affecting real-time tasks.
5. Potential For System Instability:
Elevated GPU hotspot temperatures can contribute to overall system instability.
This may manifest as crashes, system freezes, or unexpected shutdowns, especially during resource-intensive workloads.
6. Restricted Overclocking Margins:
Enthusiasts engaging in overclocking may discover that high hotspot temperatures limit the headroom for additional overclocking. Increased temperatures make it difficult to achieve stable overclocks without encountering thermal limitations.
7. Risk Of Permanent Damage:
Excessive temperatures, particularly beyond specified limits, risk permanent damage to the GPU. Over time, elevated temperatures can cause irreversible harm to the silicon and other sensitive components, rendering the GPU non-functional.
8. Heightened Fan Noise:
GPU fans may operate at increased speeds to cope with high temperatures, resulting in elevated fan noise. This can lead to a less enjoyable and louder computing experience, particularly during gaming sessions.
9. Impact On Adjacent Components:
Elevated GPU temperatures can raise the overall temperature inside the computer case.
This can influence the performance and lifespan of other components, such as the CPU, motherboard, and power supply.
10. Increased Energy Consumption:
GPUs operating at high temperatures often consume more power.
This heightened power consumption contributes to increased energy bills and places additional strain on the power supply unit.
Tips For Managing GPU Hotspot Temperature: Heat Management Mastery: Proven Tips:
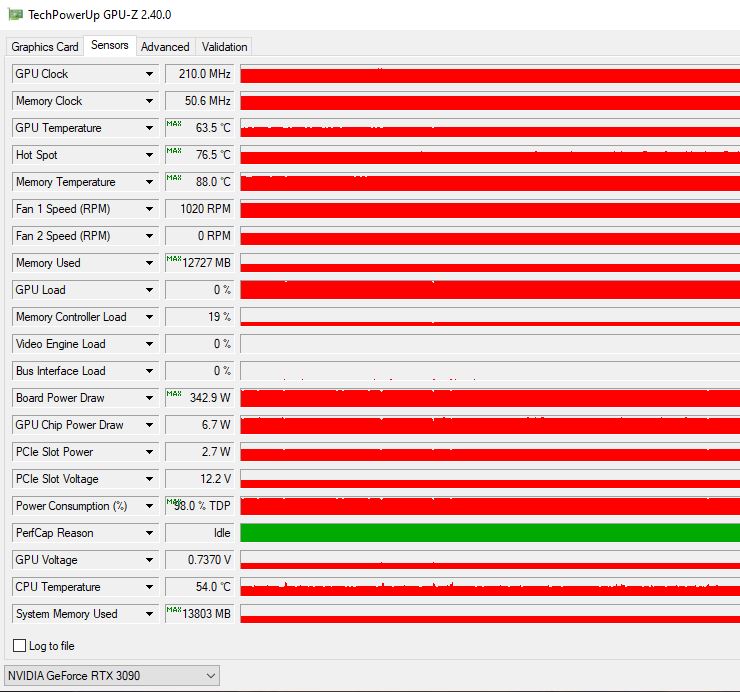
1. Prevent Elevated Temperatures Due To Dust:
- Accumulated dust on GPU fans and heatsinks can hinder airflow, increasing temperatures.
- Regularly clean your GPU and adjacent components to avoid dust buildup and sustain efficient cooling.
2. Enhance Case Ventilation:
- Organize case fans to establish positive airflow, effectively channelling cool air into the case and expelling hot air.
- Consider adding extra case fans if needed to enhance overall ventilation.
3. Monitor And Manage Temperature Levels:
- Utilize monitoring tools like HWiNFO, HWMonitor, or GPU-Z to monitor GPU temperatures, including the hotspot temperature.
- Configure alerts to notify you when temperatures approach critical levels.
4. Customize Fan Curves:
- Tailor GPU fan curves using software tools to ensure fans respond appropriately to temperature fluctuations.
- Adjusting fan speeds can enhance heat dissipation, though it may lead to increased fan noise.
5. Exercise Caution With Overclocking:
- While overclocking can boost performance, pushing the GPU to extreme levels may elevate temperatures significantly.
- Strike a balance between performance gains and temperature control when overclocking.
6. Control Ambient Temperature:
- Maintain a moderate ambient room temperature to aid overall system cooling.
- High room temperatures can contribute to elevated GPU temperatures, impacting thermal performance.
7. Explore Liquid Cooling Solutions:
- Consider liquid cooling solutions like all-in-one (AIO) coolers for efficient GPU cooling.
- Liquid cooling systems expedite heat transfer from the GPU more effectively than air coolers.
8. Apply High-Quality Thermal Paste:
- If comfortable with hardware maintenance, apply high-quality thermal paste to ensure optimal thermal conductivity between the GPU die and heatsink.
9. Review And Optimize GPU Usage:
- Be mindful of resource-intensive applications and games that strain the GPU.
- Optimize in-game settings and consider reducing graphical demands for demanding titles.
10. Upgrade To A More Efficient GPU:
- If your current GPU consistently experiences high temperatures, consider upgrading to a newer model with improved thermal efficiency.
- Newer GPU architectures often incorporate enhanced cooling solutions and superior thermal management.
11. Ensure Adequate Power Supply:
- A stable and efficient Power Supply Unit (PSU) contributes to overall system stability and lower GPU temperatures.
- Ensure that your PSU meets the power requirements of your GPU and possesses a good efficiency rating.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, monitoring the temperature of your GPU is a critical aspect of assessing the health of your graphics card and optimizing overall system performance.
Understanding the intricacies of this metric enables users to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to manage temperature effectively.
Tools such as HWiNFO, HWMonitor, and GPU-Z offer real-time insights for timely interventions. Elevated temperatures surpassing the 110°C threshold can jeopardize hardware’s performance and longevity, necessitating users to implement preventive strategies.
The journey culminates with practical tips outlined in ‘Heat Management Mastery: Proven Tips,’ which covers areas such as optimizing airflow, regular cleaning routines, and careful overclocking. This comprehensive approach ensures sustained GPU performance and enhances hardware reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What Is The Safe Range For Gpu Hotspot Temperature?
Ideally, GPU hotspot temperature should stay below 110°C to prevent potential damage, with 95°C being a generally safe upper limit for optimal performance.
2. Can High Gpu Hotspot Temperatures Damage My Gpu?
While GPUs can throttle down to prevent damage, consistently high hotspot temperatures may impact long-term performance and hardware longevity, especially during overclocking.
3. Why Does GPU hotspot Temperature Vary Among Manufacturers?
Different GPU manufacturers have varying temperature limits based on design and technology, with factors like cooling solutions and overclocking capabilities influencing these differences.
4. Is There A Correlation Between Gpu Hotspot And Average Die Temperatures?
The GPU hotspot temperature is often higher than the average die temperature. Understanding this relationship helps gauge the overall thermal health of the GPU during operation.
Read More: