How To Tell How Long A GPU Has Been Used – Complete Guide
Imagine easily looking into your computer’s core to understand the age and health of its parts. Among these crucial gaming or graphic design components is the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), a vital but often mysterious element.
To determine a GPU’s cumulative usage time, use third-party tools like MSI Afterburner or HWiNFO for historical data, as Task Manager only provides real-time information. Check system uptime, logs, BIOS, and inquire with the previous owner for insights, but exact usage figures may be challenging to obtain.
Join us as we explore the world of technology and learn how to determine the usage duration of a GPU on our enlightening journey.
The Significance Of Tracking GPU Usage For Optimal Performance: Unlocking Insights:
1. Performance Optimization:
Monitoring GPU usage provides real-time insights into hardware efficiency, which is crucial for tasks like gaming or resource-intensive applications. It helps optimize performance by identifying usage patterns, allowing adjustments to match task demands and ensure smooth operation.
2. Temperature Management:
Temperature management is vital, as excessive GPU usage can increase temperatures, impacting performance and longevity. Monitoring allows users to implement cooling solutions, preventing overheating and thermal throttling and adjust fan speeds based on temperature trends.
3. Identifying Bottlenecks:
Identifying bottlenecks is facilitated through GPU usage monitoring, helping address mismatches in hardware capabilities. This ensures a balanced system, preventing the GPU from consistently operating at maximum capacity while other components are underutilized.
4. Diagnosing Performance Challenges:
Troubleshooting performance issues is made more accessible by tracking GPU usage patterns. Drops or spikes may indicate underlying problems, such as malfunctioning GPUs, outdated drivers, or conflicting software. This data aids in diagnosing and resolving issues promptly.
5. Energy Efficiency:
For energy-conscious users, tracking GPU usage helps manage power consumption effectively. Understanding the relationship between workload and energy usage allows adjustments to strike a balance between performance and energy efficiency, especially relevant for laptops and those aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
6. Extended Hardware Lifespan:
Consistently high GPU usage can lead to wear and tear. Monitoring usage patterns allows users to implement strategies to extend GPU lifespan, such as setting usage limits, optimizing cooling, or scheduling maintenance for long-term reliability.
7. Optimal Resource Allocation:
In multi-GPU setups, tracking usage ensures optimal resource allocation. Understanding which applications use the GPU enables effective allocation, maximizing performance for specific tasks without unnecessary strain on the hardware.
Essential Software Tools To Monitor GPU Usage: Optimizing Performance:
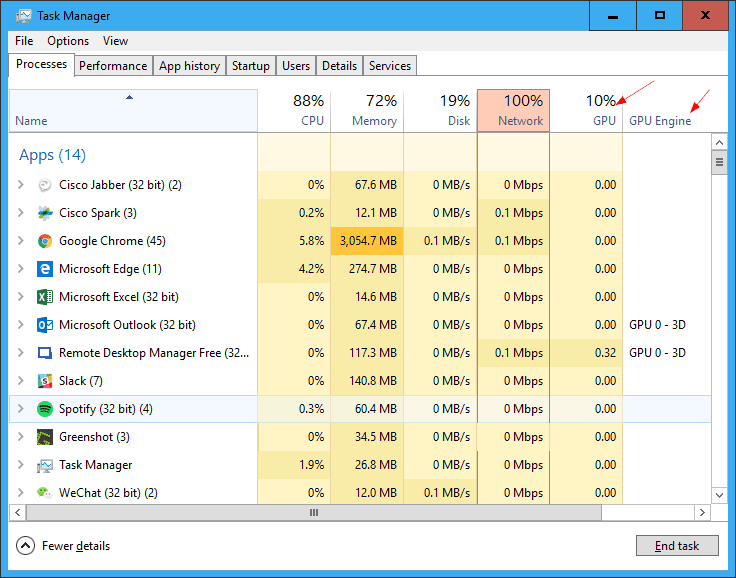
1. Task Manager For Current Usage:
- The integrated Task Manager in Windows is a convenient tool for a quick overview of present GPU utilization.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch Task Manager, go to the “Performance” tab, and select “GPU.”
- Here, you can monitor the GPU’s ongoing utilization, dedicated video memory, and overall usage by various applications.
2. Benchmark Performance:
Benchmarking tools like 3DMark or Unigine Heaven offer comprehensive insights into your GPU’s performance under varied workloads. These tools execute standardized tests, measuring frame rates, rendering capabilities, and overall efficiency. Comparing benchmark results over time aids in evaluating any performance deterioration.
3. Check System Information:
- Windows’s integrated System Information tool provides a wealth of data about your system components, including the GPU. Press Win + R, type “msinfo32,” and press Enter.
- Navigate to “Components” and then “Display” to locate detailed information about your GPU, including the driver version and date.
4. Gpu-Z:
GPU-Z is a specialized tool crafted for thorough GPU monitoring. It supplies real-time data on GPU specifications, temperature, usage, and more. GPU-Z is invaluable for enthusiasts and professionals seeking detailed insights into their GPU’s performance. Download it from the official website and explore its abundance of information.
5. Check Warranty Information:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website to authenticate your GPU’s warranty details and gain insights into its age.
- Input the GPU’s serial number, usually located on the card or packaging, to determine the remaining warranty period.
- While not a monitoring tool, warranty information is crucial for assessing the GPU’s history.
6. Monitoring Software For Historical Data:
Applications like MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, or CAM by NZXT provide real-time monitoring of GPU usage, temperature, and fan speed. Additionally, they log historical data, enabling users to analyze performance trends over time. Customizable alerts in these tools can notify users of abnormal usage or temperature spikes.
7. Logs And Bios Information:
- Accessing advanced users’ system logs and BIOS information can yield more profound insights into GPU behavior.
- System logs record events, errors, and warnings related to the GPU, while BIOS information contains details about the GPU’s firmware.
- Exercise caution when exploring these areas, and consider seeking expert advice if you need to become more familiar with advanced system settings.
8. System Uptime:
Monitoring the overall system uptime is a straightforward yet effective way to assess the continuous usage of your GPU. A lengthier system uptime may indicate prolonged periods of GPU operation, providing context for performance trends.
9. Purchase Or Installation Date:
- While not a software tool, keeping tabs on the GPU’s purchase or installation date is crucial for understanding its lifespan.
- This information, coupled with monitoring tools, aids users in making informed decisions about potential upgrades or replacements.
Exploring Physical Indicators Of GPU Usage In Hardware: Decoding Performance:
1. Communication With Previous Owner:
When buying a used GPU, talking to the previous owner is essential. Whether online or local, ask about its history – what it was used for, types of applications/games, and if it was overclocked. Learning about the user’s habits and maintenance can give insights into how well the GPU was handled.
Questions To Consider:
- What was the primary use of the GPU?
- Were there any overclocking practices?
- How frequently was the GPU cleaned or maintained?
2. Inspect Physical Wear And Tear:
When getting a used GPU, thoroughly examine its physical condition for signs of wear or potential problems. Pay close attention to:
- Dust Accumulation: Dust can build up on the cooling fans and heat sinks over time, blocking airflow and causing overheating. Check for dust and clean the cooling solution if needed.
- Fan Condition: Ensure the fans are spinning freely and without strange noises. Damaged or worn-out fans can result in insufficient cooling.
- Connectors And Ports:
Check for bent or damaged connectors on the GPU. Examine the HDMI, DisplayPort, or other video output ports for any signs of wear.
- Thermal Paste:
Thermal paste is crucial for efficient heat transfer between the GPU chip and the heatsink. Dry or worn-out thermal paste can lead to inadequate heat dissipation. Consider reapplying thermal paste if necessary.
- Capacitors And Components:
Inspect the GPU’s circuit board for visible damage, burnt areas, or leaking capacitors. Damaged components may indicate potential issues.
- GPU Backplate:
Some GPUs come with backplates that contribute to structural integrity and cooling. Examine the backplate for any bends, cracks, or signs of damage.
- Overall Physical Condition:
Evaluate the GPU’s general physical condition, including scratches, dents, or other cosmetic damage. While cosmetic issues may not directly affect performance, they can provide additional insights into the card’s history.
Top Tips For Buying A Used GPU: A Comprehensive Guide:

1. Research The Model:
- Understand the specifications, benchmarks, and typical pricing of the GPU model.
- Helps assess the value of the used GPU.
2. Check The Seller’s Reputation:
- Verify the reputation and reviews of the seller on platforms like eBay or forums.
- A reputable seller is more likely to provide accurate information about the GPU’s condition.
3. Communicate With The Seller:
- Engage in a conversation to gather information about the GPU’s usage history.
- Inquire about primary use, overclocking practices, and maintenance routines.
4. Inspect Physical Condition:
- Carefully examine the GPU for damage, such as bent connectors, scratches, or dents.
- Check the cooling solution for dust accumulation and the condition of the fans.
5. Ask For Benchmark Results:
- Request benchmark results or performance metrics from the seller.
- Compare provided benchmarks with standard performance metrics for the specific model.
6. Check Warranty Information:
- Verify if the GPU is still under warranty.
- Use the original purchase receipt or packaging to check the warranty status on the manufacturer’s website.
7. Test The GPU:
- Test the GPU’s performance in real-world scenarios, such as running graphics-intensive applications or games.
- Helps identify potential issues not apparent during a visual inspection.
8. Request Original Accessories:
- If available, request the original packaging and accessories.
- Original accessories, like the anti-static bag, indicate proper maintenance and storage.
9. Negotiate The Price:
- Feel free to negotiate, mainly if minor issues are found or the GPU is nearing the end of its warranty.
- Be aware of current market prices for similar used GPUs for informed negotiations.
10. Be Cautious Of Mining Gpus:
- Exercise caution if the GPU was previously used for cryptocurrency mining.
- Mining GPUs may have been under constant load, potentially impacting lifespan.
- Check for signs of wear and tear associated with prolonged usage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, monitoring GPU usage is essential to maintaining optimal performance in any computer system. This article has highlighted the significance of tracking GPU usage and discussed various software tools that aid in this process. With these tools, users can unlock valuable insights about their GPU’s longevity and performance efficiency. They can identify potential issues early on and take necessary actions to prolong the lifespan of their GPU. Therefore, users are encouraged to regularly track their GPU usage for a smooth, efficient computing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How Do I Interpret GPU Temperature Data?
GPU temperature data helps assess the cooling efficiency and potential for thermal throttling. Generally, temperatures below 80-85 degrees Celsius are safe, but optimal ranges can vary based on the GPU model.
2. How Can I Prolong The Lifespan Of My Gpu?
To extend GPU lifespan, maintain optimal temperatures through proper cooling, avoid excessive overclocking, clean the GPU regularly to prevent dust buildup, and ensure a stable power supply. Monitoring software can help track usage and temperatures for proactive maintenance.
3. Are There Signs That My GPU Has Been Extensively Used?
Yes, signs such as frequent crashes, graphic glitches, or overheating could indicate prolonged usage.
4. Can I Extend The Lifespan Of My Graphics Card By Moderating Its Usage?
Yes, managing the workload of your graphics card (like avoiding running graphically-intensive tasks continuously) can help extend its lifespan.
5. Can My PC’s Performance Be Affected If My Graphics Card Has Been Overused?
An overused or failing graphics card can cause system instability and poor overall PC performance.
Read More: