Gpu At 100 When Idle – Causes And Solutions In 2024
As tech evolves, we depend more on GPUs for gaming and content creation tasks. When they act up, users get frustrated.
If your GPU is consistently at 100% when idle, update drivers, check for malware, close unnecessary processes, update your operating system, and monitor GPU temperatures. If the issue persists, seek help from your GPU manufacturer’s support.
Join us as we explore and provide you with the necessary knowledge to address this puzzling issue effectively.
Understanding Gpu And Its Typical Idle Temperature:
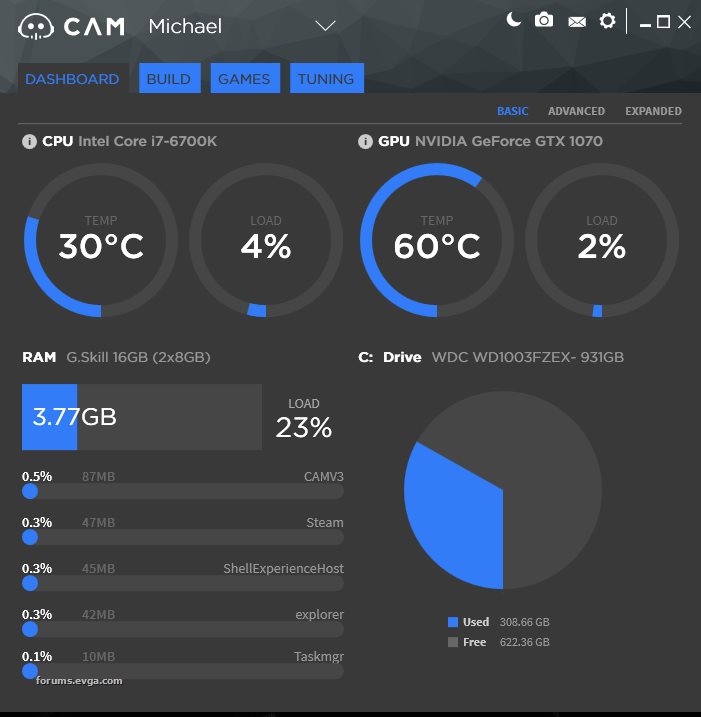
The GPU, or graphics processing unit, is an essential component of modern computer systems and is responsible for rendering images and videos.
However, when a GPU is running at 100% capacity even while idle, it can indicate potential issues that need to be addressed. Understanding the typical idle temperature for a GPU is crucial in diagnosing this problem.
A properly functioning GPU should typically have an idle temperature between 30 to 40 degrees Celsius.
When the GPU reaches 100% capacity at such low demand times, it could be due to background tasks using up resources or defective hardware components. This anomaly can increase power consumption and unnecessary wear on the GPU’s components.
Causes Of Gpu Temperature At 100 When Idle: Unveiling The Culprits:
1. Airflow Restrictions:
Inadequate airflow within the computer case can lead to the stagnation of hot air, causing components to overheat. Ensure that fans are correctly positioned and that no obstructions hinder the airflow.
2. Dust Accumulation:
- Dust Buildup: Over time, dust can accumulate on cooling components, such as fans and heat sinks, impeding their efficiency. Regular cleaning is vital to prevent thermal issues.
- Faulty Or Inefficient Cooling Fans:
A malfunctioning or slow-spinning cooling fan can result in poor heat dissipation. Verify the functionality of fans and replace any that are not operating correctly.
- Insufficient Number Of Fans: A computer may sometimes need more fans to dissipate heat efficiently. Consider adding extra fans or upgrading existing ones.
3. Degradation Of Thermal Paste:
Over the course of time, the thermal paste situated between the CPU/GPU and the heatsink may experience deterioration, leading to a decline in its thermal conductivity and overall effectiveness.Reapplying high-quality thermal paste can enhance heat transfer and lower temperatures.
4. Overclocking:
Pushing hardware components beyond their recommended limits through overclocking can significantly increase heat generation. Revert to default clock speeds or consider more efficient cooling solutions.
5. Background Processes And Applications:
Specific background processes or applications may consume significant system resources, leading to increased temperatures during idle periods. Identify and close unnecessary procedures to reduce thermal load.
6. Ambient Temperature And Environment:
The external environment can impact internal temperatures. Ensure that the computer is placed in a well-ventilated area, and consider ambient temperature when assessing idle temperatures.
7. Outdated Or Faulty Hardware:
- Aging Components: Outdated hardware, such as an old CPU or GPU, may need help to handle modern software efficiently, resulting in increased temperatures. Consider upgrading hardware components if they need to be updated.
- Hardware Failure: Malfunctioning components, such as a failing power supply or motherboard, can contribute to elevated temperatures. Diagnose and replace faulty hardware to restore normal thermal conditions.
Effective Solutions For High Gpu Temperature At Idle: Optimizing Thermals:
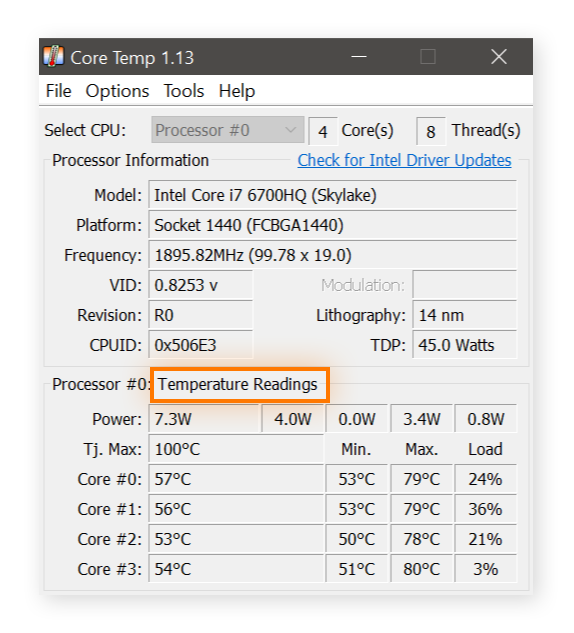
1. Inspect Task Manager Or Activity Monitor:
- Access Task Manager on Windows or Activity Monitor on macOS.
- Identify processes or applications that may be excessively utilizing the GPU.
- Terminate or close any extra operations.
2. Update Graphics Drivers:
- Ensure that your GPU drivers are current.
- Visit the official website of your GPU manufacturer (NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel) and download the latest drivers.
3. Scan For Malware:
- Malicious software could be causing heightened GPU activity.
- Conduct a thorough system scan using your antivirus software to confirm the cleanliness of your system.
- In addition to scanning for malware using traditional antivirus tools, it’s also worth considering specialized anti-malware programs designed specifically for intensive system scans.
4. Check For Windows Updates:
- Ensure your operating system is current.
- Updates sometimes resolve compatibility issues that lead to elevated GPU usage.
5. Monitor Background Processes:
Utilize tools such as Process Explorer (on Windows) or Activity Monitor (on macOS) to pinpoint any background processes utilizing the GPU.
6. Identify Rogue Applications:
- Specific applications may have memory leaks or other issues causing excessive GPU resource usage.
- Experiment with closing applications one at a time to identify any particular culprits.
7. Temperature And Cooling:
- Evaluate your GPU’s temperature.
- Elevated temperatures can result in increased fan speeds and power consumption.
- Confirm the proper functioning of your GPU cooling system and ensure that vents are unobstructed.
8. Power Settings:
- Examine your computer’s power settings.
- High-performance power plans can force the GPU to operate at maximum capacity, even during idle periods.
- Consider switching to a balanced or power-saving plan.
9. Bios/Uefi Update:
- Confirm that your motherboard’s BIOS or UEFI firmware is up-to-date.
- To update your BIOS/UEFI, first identify your motherboard model and visit the manufacturer’s official website to download the latest firmware version.
- Once downloaded, carefully follow the instructions to update the BIOS/UEFI safely.
- It’s crucial to exercise caution during this process, as any errors or interruptions could potentially lead to irreversible damage to your system.
Understanding The Impact Of High Gpu Temperature At Idle On System Performance: Assessing The Consequences:
1. Reduced Performance:
High temperatures can cause thermal throttling, a protective measure that slows down the CPU or GPU to prevent overheating. This leads to lower processing power and overall system performance.
2. Increased Fan Noise:
Fans work harder and faster to cool down the system in response to rising temperatures. This can result in louder fan noise, which might be distracting in quiet places or indicate an issue with the cooling system.
3. Shortened Hardware Lifespan:
Exposure to high temperatures for a long time can wear out electronic components. This can lead to a shorter lifespan for the CPU, GPU, and other sensitive hardware, potentially requiring more frequent replacements.
4. System Instability And Crashes:
Excessive heat can make the system unstable, causing unexpected crashes, freezes, or even shutdowns. This can result in data loss and disrupt ongoing tasks.
5. Risk Of Permanent Damage:
Sustained high temperatures can permanently damage the CPU and GPU. Over time, this can show reduced performance, more errors, and, in extreme cases, complete hardware failure.
6. Increased Energy Consumption:
As the cooling system works harder to dissipate heat, the overall energy consumption of the system may go up. This can contribute to higher electricity bills and a more significant environmental impact.
7. Negative Impact On Surrounding Components:
High temperatures can affect nearby components, potentially impacting the reliability and performance of other hardware components on the motherboard.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the typical idle temperature of a GPU is crucial for maintaining its optimal performance and longevity.
The causes of a GPU temperature reaching 100 when idle can vary from inadequate cooling systems to software issues.
However, practical solutions such as improving ventilation, updating drivers, and monitoring background processes can help mitigate high GPU temperatures at idle.
It is essential to recognize the impact of high GPU temperatures on system stability and component lifespan and address any issues promptly.
Users can ensure their systems run smoothly and efficiently by implementing these solutions and staying vigilant about GPU temperatures. Take proactive steps to monitor and manage your GPU’s temperature to prevent potential hardware damage in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What If Gpu Temperatures Remain High After Troubleshooting?
If issues persist, seek assistance from your GPU manufacturer’s support forums or consult a hardware professional for in-depth troubleshooting and solutions.
2. Is There Specific Software That Commonly Causes Gpus To Reach 100% Usage When Idle?
Some video editing software, cryptocurrency mining programs, and poorly optimized games can contribute to high GPU usage even when not actively used.
3. Should I Consider Replacing My GPU if It Consistently Runs At 100% When Idle?
If all troubleshooting steps fail and the problem persists despite standard usage patterns, consider replacing the GPU with professional advice from a technician.
4. Is It Normal For A GPU to Run At 100% Utilization While Idling?
No, it’s not normal. High GPU usage during idle periods indicates an issue that needs troubleshooting.
Read More: