Gpu Power Consumption Drops || Reasons & Solutions In 2023
In the world of super-fast computers, it can be unclear when the power usage of your computer’s graphics processor suddenly goes down. This can be a problem for people who want their computer to work at its best
Power supply unit (PSU) limitations, memory clock instability, overclocking issues, bad motherboard connections, inadequate cooling, power management settings, use of integrated GPU, driver issues, crossfire/sli configurations, CPU bottlenecks, software conflicts and background processes, faulty video drivers, and power-saving modes are the reasons behind GPU power consumption drops.
This article discusses solutions for unexpected drops in GPU power consumption, offering a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting hardware and software issues.
Understanding The Reasons Behind GPU Power Consumption Drops:
1. Power Supply Unit (PSU) Limitations:

Sometimes, a computer’s power supply (PSU) can’t give enough power to the graphics card (GPU), causing its performance to drop.
This happens when the GPU needs more power than the PSU can provide, making the computer unstable and even harming the GPU and other parts.
2. Memory Clock Instability:
An essential reason for GPU power drops is an unstable memory clock. Memory clocks control how quickly a graphics card accesses data from its memory.
When these clocks become unstable, it causes the GPU to use more power than needed. Fluctuating memory clock frequencies make the GPU constantly adjust voltage levels, leading to higher energy usage and heat generation.
3. Overclocking Issues:
Recently, there’s been a lot of talk in the gaming and PC-building community about GPU power drops. One possible reason is linked to overclocking, where users push their graphics card beyond its normal limits for better performance.
While this can enhance gaming, it also makes the GPU use more power. Overclocking requires higher voltage, leading to increased energy consumption and heat generation. The GPU’s cooling system, like fans or liquid cooling, has to work even harder, consuming more energy to cool down.
4. Bad Motherboard Connections:
The delivery of power is pivotal, and the motherboard plays a crucial role in this function.Weak connections between the GPU and motherboard can result in power inefficiencies, leading to reduced GPU power during demanding tasks.
5. Inadequate Cooling:
Powerful graphics cards generate significant heat, so they require efficient cooling systems to maintain optimal performance.
When the cooling system fails or is insufficient, the GPU tends to throttle its power consumption to prevent overheating.
This drop in power consumption ensures that the GPU operates within safe temperature limits, although it may result in reduced performance and lower clock speeds.
6. Power Management Settings:
GPU power can drop due to idle time, meaning it lowers its energy use when it’s not working hard. Modern GPUs also balance tasks among processors, so some can rest while others work, saving power.
Advanced techniques like clock gating turn off parts of the GPU not in use, and dynamic voltage scaling adjusts energy based on workload, helping to save power.
7. Use Of Integrated GPU:
One reason behind the drop in power consumption is the improved efficiency of integrated GPUs. Due to their high-performance capabilities, traditional discrete graphics cards often consume significant amounts of power.
However, with technological advancements, manufacturers have achieved similar performance levels with integrated GPUs while significantly reducing power consumption.
8. Driver Issues:
When GPU manufacturers release new drivers, they often optimize their GPUs’ performance and power consumption. Users who update their graphics card drivers may experience decreased power consumption.
9. Crossfire/Sli Configurations:
In setups where multiple GPUs are arranged in CrossFire or SLI, problems in communication between the GPUs can result in power reductions. Ensuring the correct configuration and compatibility is crucial to prevent these issues.
10. Cpu Bottlenecks:
When the CPU isn’t strong enough to match the demands of the GPU, it can cause a bottleneck, meaning the GPU isn’t fully used. This difference in processing power can result in reduced GPU performance and power drops.
11. Software Conflicts And Background Processes:
Unneeded services, background apps, or conflicts between software can use up system resources and impact GPU performance, causing power drops.
12. Faulty Video Drivers:
Video drivers connect the GPU and the operating system. Problems with these drivers can affect how well the GPU works, leading to drops in power consumption.
13. Power-Saving Modes:
Power-saving features in the operating system or GPU drivers can lead to reduced power consumption to conserve energy. Disabling these modes might be necessary for optimal GPU performance.
Solutions To Address GPU Power Consumption Drops:
1. Stable Overclocking:
One solution to address GPU power consumption drops is implementing stable overclocking techniques. Users can enhance their GPUs’ performance by carefully increasing the clock speed and voltage settings while maintaining a steady power supply.
This allows the GPU to run at higher rates without experiencing sudden drops in power consumption. However, it’s important to note that stable overclocking requires thorough testing and monitoring to ensure the GPU remains within safe temperature limits.
2. Verify Psu Adequacy:
Verifying that your PSU can deliver sufficient power to your graphics card is crucial. Often, users need to pay more attention to this aspect and opt for a lower-wattage PSU, which can significantly drop GPU performance.
Upgrading to a higher wattage PSU that meets the recommended requirements of your GPU can help address this issue.
3. Memory Clock Adjustments:
If memory clock instability is suspected, adjust the memory clock settings. Experiment with slightly lowering the memory clock to see if it resolves power consumption drops without compromising performance significantly.
4. Check Motherboard Connections:
One potential solution to address GPU power consumption drops is to check the motherboard connections.
Often, loose or improper connections between the graphics card and the motherboard can result in power disruptions, leading to drops in GPU performance.
Checking the physical connection between these components and ensuring they are securely attached can help resolve this issue.
5. Optimize Cooling Solutions:
Overheating reduces performance and power efficiency.GPU throttles speed to prevent damage.
Follow these processes:
1. Efficient Cooling Mechanisms:
- Use high-quality thermal paste.
- Ensure proper air ventilation.
- Implement enhanced heat sinks.
2. Undervolting the GPU:
- Default voltage settings are often higher than necessary.
- Reducing voltage lowers power consumption without affecting performance.
- It helps address power consumption and reduces heat generation.
3. Optimizing Fan Curves:
- Fan curves regulate temperature by adjusting the fan speed.
- Balance cooling and noise levels.
- Efficiently operate fans when needed without unnecessary fluctuations.
6. Adjust Power Management Settings:
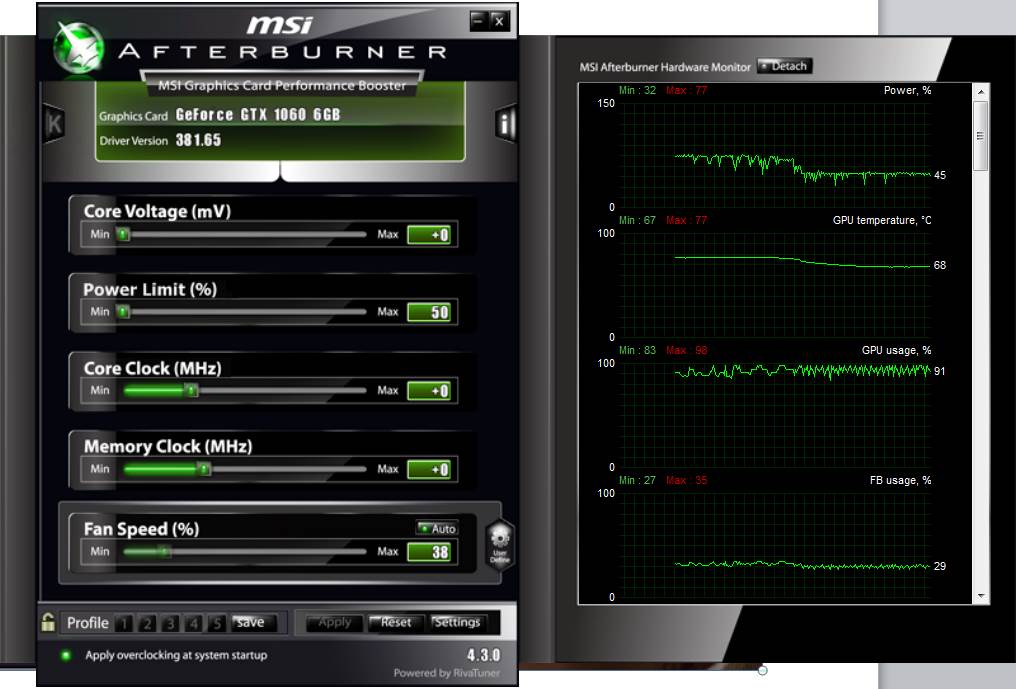
Default GPU settings are often in balanced or energy-saving mode. These modes limit performance and reduce power consumption. Changing settings to prioritize maximum performance can prevent sudden drops.
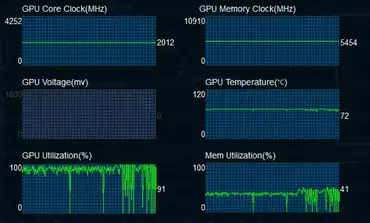
Utilize Advanced Monitoring Software:
- Specialized tools offer real-time data on GPU parameters.
- Parameters include power consumption, temperature, and clock speeds.
- It helps users analyze and optimize GPU power usage.
- Identifies fluctuations or abnormalities in GPU performance during critical tasks.
7. Update GPU Drivers:
Manufacturers release driver updates regularly to fix bugs, improve performance, and enhance power management for their GPUs.
By staying up-to-date with the latest driver versions, you ensure that your GPU’s power consumption is optimized and that any issues causing drops in power consumption are resolved.
8. Verify Crossfire/Sli Configurations:
n systems featuring multiple GPUs, ensure effective communication and compatibility among the GPUs. It is advisable to conduct tests using a single GPU to determine if any issues are arising from the CrossFire/SLI configuration.
9. Address Cpu Bottlenecks:
Upgrade the CPU if it is identified as a bottleneck. A well-balanced system ensures the GPU can operate at its full potential without power drops.
10. Minimize Background Processes:
When running intense graphics-heavy applications, closing any unnecessary programs or services running in the background is crucial.
These processes can consume a significant amount of power and put additional strain on the GPU, leading to power consumption and performance drops.
By closing these background processes, you can ensure that the GPU focuses solely on the task at hand, maximizing its power efficiency.
11. Resolve Software Conflicts:
This can be done by regularly updating all installed applications and ensuring their compatibility. Closing unnecessary background processes and optimizing power settings for specific software can mitigate conflicts and maintain a stable power consumption level.
12. Ensure Video Driver Stability:
Verify the stability of video drivers by reinstalling them. Use a reliable driver removal tool to ensure a clean uninstallation before installing the latest drivers compatible with your GPU model.
13. Disable Power-Saving Modes:
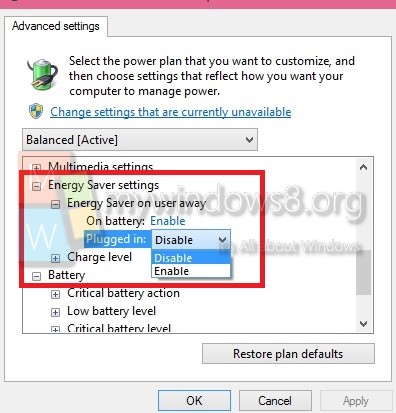
Power-saving features such as Nvidia’s PowerMizer Technology or AMD’s PowerPlay are designed to reduce power consumption when the GPU is not under heavy load.
1. Nvidia Graphics Card:
- Access the Nvidia Control Panel.
- Go to Power Management Mode.
- Choose “Prefer maximum performance” instead of “Adaptive.”
2. AMD Graphics Card:
- Open Radeon Settings.
- Adjust performance level using the Power Limit Slider.
14. Avoid Using Integrated GPU:
To disable integrated GPU:
- Access your system’s BIOS settings and disable integrated graphics.
- This ensures that your system relies solely on the dedicated GPU, minimizing the chance of power drops.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the power consumption of GPUs has seen a significant drop in recent years, alleviating some of the limitations imposed on power supply units (PSUs).
This reduction in power consumption has also helped address issues like memory clock instability and overclocking problems.
Additionally, technological advancements have led to improvements in motherboard connections, ensuring reliable and stable performance.
Inadequate cooling is another factor that can be mitigated with better GPU designs and more efficient cooling solutions.
Lastly, users can optimize their power management settings to enhance performance and stability. As the GPU industry evolves, users must stay informed about these developments and use them to maximize their gaming or computing experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How Can I Check If My Psu Is Causing Gpu Power Drops?
Verify your PSU’s capacity to meet the GPU’s power requirements. Upgrading to a more robust PSU may be necessary if it struggles to provide stable power during demanding tasks.
2. Should I Consider Upgrading My Cpu To Prevent Gpu Power Drops?
If your CPU is identified as a bottleneck, upgrading to a more powerful CPU can help balance the load and prevent power drops during demanding tasks.
3. Can Antivirus Background Activity Impact GPU Performance?
Yes, active antivirus scans and background activity can divert resources. Temporarily disabling antivirus protection may help determine if it is contributing to GPU power drops.
4. Can Improper Game Settings Lead To GPU Power Drops?
Yes, if game settings are too demanding for your GPU, it can lead to power drops. Optimize in-game settings to achieve a balance between visual quality and GPU performance.
5. When Should I Seek Professional Assistance For GPU Power Consumption Issues?
If you’ve tried the suggested solutions and issues persist, or if you have specific concerns about your GPU, seeking help from professional technicians or contacting your GPU manufacturer’s support is advisable.