How To Use Both Gpu And Integrated Graphics – Complete Guide
Are you tired of feeling like your computer’s graphics performance is holding you back? Do you want to unlock the full potential of both your discrete GPU and integrated graphics?
Check Device Manager for integrated and dedicated GPU drivers, enable integrated graphics in the BIOS if needed, and then connect the second monitor to utilize both GPUs on Windows automatically.
The article guides you on effectively maximizing system performance using GPU and integrated graphics.
Understanding Gpu And Integrated Graphics:

Using GPU (dedicated graphics) and integrated graphics through GPU passthrough can boost computer performance.
This involves assigning specific tasks to each graphics processor, combining the processing power of a dedicated GPU with the energy efficiency of integrated graphics.
This approach improves multitasking by dedicating intensive graphical tasks like gaming to the dedicated GPU while running less demanding applications on integrated graphics. The result is smoother performance across various applications and an enhanced user experience.
This dual GPU setup maximizes system performance and conserves energy during lighter tasks, providing greater control over the computing experience and seamless transitions between different usage scenarios.
How To Set Up Both GPU And Integrated Graphics: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Check Compatibility Of Hardware:
- Before you try using your GPU and integrated graphics, ensure your hardware supports this setup.
- Most modern motherboards and processors easily allow the integration of both graphic solutions.
2. Access Bios/UEFI Settings:
- To get started, access your computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Press the designated key (often Del, F2, or Esc) during the boot process to enter the settings.
- Once inside, go to the “Advanced” or “Integrated Peripherals” section.
3. Enable Integrated Graphics:
- Find the “Integrated Graphics,” “iGPU,” or a similar option and make sure it’s enabled.
- This activates the integrated graphics component of your processor.
4. Configure Multi-Gpu Settings:
- In the BIOS/UEFI settings, look for an option related to Multi-GPU, Hybrid Graphics, or similar terminology.
- The wording may vary depending on your motherboard and processor.
- Enable the option that allows the simultaneous use of the dedicated GPU and integrated graphics.
5. Install GPU Drivers:
- Ensure you have the latest drivers installed for your dedicated GPU and integrated graphics.
- Visit the official websites of the GPU manufacturer (NVIDIA or AMD) and the processor manufacturer (Intel or AMD) to download and install the respective drivers.
6. Optimize Applications:
- Specific applications let users specify which graphics processor to use.
- Choose the preferred graphics processor for each application in graphics settings or control panels for applications like games or design software.
7. Monitor Gpu Usage:
- Keep an eye on GPU usage using system monitoring tools.
- This ensures that the dedicated GPU and integrated graphics actively contribute to the system’s performance.
Key Benefits Of Utilizing Both Gpu And Integrated Graphics In Your System:

1. Enhanced Performance:
Combining the strength of a dedicated GPU with the efficiency of integrated graphics elevates overall system performance, especially for graphics-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
This synergy creates a dynamic computing environment capable of handling diverse applications with enhanced speed and responsiveness.
2. Optimized Power Consumption:
Integrated graphics, known for their superior power efficiency compared to dedicated GPUs, prove ideal for everyday tasks, resulting in lower power consumption and extended battery life in laptops.
Seamlessly transitioning to integrated graphics ensures efficient power utilization when the system operates under a light graphics load.
3. Improved Multitasking:
The integration of GPU and integrated graphics enhances multitasking capabilities. The dedicated GPU manages resource-intensive applications, while integrated graphics efficiently handle less demanding tasks.
This intelligent division of labor ensures a seamless user experience, particularly when running multiple applications concurrently.
4. Seamless Graphics Switching:
Modern systems supporting dynamic graphics switching enable seamless transitions between the dedicated GPU and integrated graphics based on workload demands.
This real-time optimization ensures that the system utilizes the most appropriate graphics solution, optimizing performance and power efficiency.
5. Cost-Effective Solution:
For users whose computing needs don’t mandate the full power of a high-end dedicated GPU, relying on integrated graphics for lighter tasks and activating the dedicated GPU when necessary proves a cost-effective solution.
This approach eliminates the need for an expensive graphics card, offering efficiency without compromising performance.
6. Compatibility And Reliability:
The combination of GPU and integrated graphics enhances compatibility across various applications and software.
Older or less graphically demanding programs may function more efficiently with integrated graphics, while newer or resource-intensive applications can leverage the dedicated GPU, ensuring reliable performance across diverse scenarios.
7. Enhanced Video Playback:
Integrated graphics, optimized specifically for video playback, facilitate smooth and efficient streaming of high-definition content.
Whether watching videos or participating in video conferencing, integrated graphics take the lead, providing a superior viewing experience without imposing unnecessary strain on the dedicated GPU.
8. Future-Proofing:
They are using GPU and integrated graphics positions users to future-proof their systems. As technology progresses, software developers may optimize applications for hybrid graphics configurations.
This proactive approach ensures compatibility with upcoming software and applications that benefit from the advantages of a dual graphics setup.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Seamless Performance:

1. Driver Conflicts:
- Ensure the latest drivers for both dedicated GPU and integrated graphics.
- Consider clean installation of drivers to prevent conflicts.
- Check the official websites of hardware manufacturers (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) for updates.
2. BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Confirm integrated graphics are enabled in BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Check that Multi-GPU or Hybrid Graphics options are configured correctly.
- Refer to the motherboard’s manual for specific instructions.
3. Application-Specific Issues:
- Explore graphics settings within applications.
- Adjust settings to ensure the right graphics solution for each app.
4. Dynamic Switching Problems:
- Check system power settings and graphics switching options.
- Ensure settings permit seamless transitions between integrated and dedicated graphics.
5. Compatibility Issues:
- Verify compatibility of motherboard, CPU, and GPU for hybrid graphics.
- Check for firmware updates for the motherboard and BIOS/UEFI.
6. System Instability Or Crashes:
- Revisit BIOS/UEFI settings to align with hardware specifications.
- Consider reverting to default settings and gradually reconfiguring.
- Check for overheating issues.
7. Incomplete GPU Utilization:
- Monitor GPU usage with system monitoring tools.
- Some apps may need manual configuration to recognize and use the dedicated GPU.
- Ensure GPU is selected as the preferred graphics processor in system settings.
8. Update Operating System:
- Keep OS up-to-date with the latest updates and patches.
- Updates often include improvements addressing compatibility issues with hardware and software.
Post-Configuration Precautions: Ensuring Stability After Using Both Gpu And Integrated Graphics:
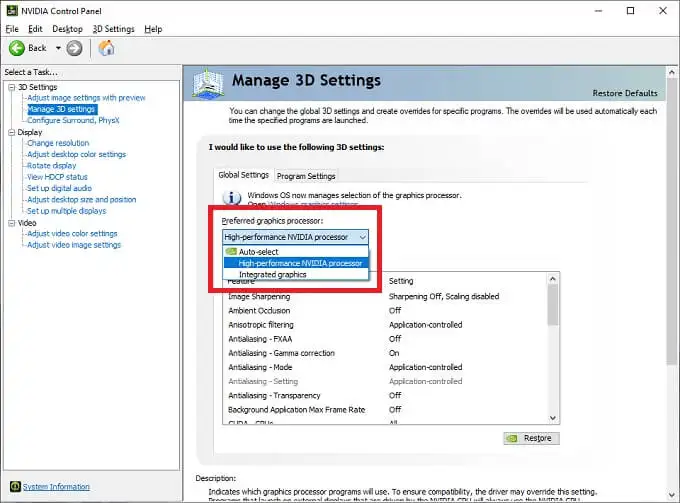
1. System Performance Monitoring:
- Regularly check system performance, especially during graphics-intensive tasks.
- Use monitoring tools for CPU and GPU temperatures, fan speeds, and overall resource usage.
2. Driver Updates:
- Stay proactive in updating both dedicated GPU and integrated graphics drivers.
- Benefit from bug fixes, optimizations, and improved compatibility.
3. Cooling Maintenance:
- Ensure proper cooling to dissipate heat from GPU and integrated graphics.
- Clean fans and heat sinks regularly to prevent dust buildup.
4. Application Settings:
- Periodically verify graphics settings within applications.
- Confirm the correct graphics processor is selected for each application.
5. Backup System Configuration:
- Create a backup or restore point after configuring GPU and integrated graphics.
- Allows reverting to a stable state in case of unforeseen issues.
6. Os And Firmware Updates:
- Regularly update the operating system for compatibility and security.
- Check for motherboard and BIOS/UEFI firmware updates for stability and features.
7. System Stability Testing:
- Occasionally, stress-test the system with benchmarking tools.
- Identifies potential issues during intense graphics processing tasks.
8. Documentation:
- Maintain a log of changes to system configuration, BIOS/UEFI settings, and driver updates.
- Serves as a reference for troubleshooting and adjustments.
9. Power Supply Verification:
- Periodically check the power supply unit for sufficient power.
- Ensure it meets the power requirements, especially after hardware changes.
10. Prompt Issue Addressing:
- Address abnormal behavior, crashes, or performance degradation promptly.
- Troubleshoot components, check for updates and consult support forums if needed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding how to utilize both GPU and integrated graphics can significantly enhance the performance and versatility of your computer system.
By learning how to set up both GPU and integrated graphics, you can take advantage of the strengths of each to optimize your computing experience.
The key benefits of utilizing GPU and integrated graphics include improved multitasking capabilities, enhanced video editing and gaming experiences, and efficient power management.
It is essential to explore the potential of both GPU and integrated graphics to harness the capabilities of your system entirely.
Take the time to experiment with different settings and configurations to find the balance that best suits your needs and unlock the full potential of your computer’s graphics capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Are There Specific Applications That Benefit From Using Both Graphics Options?
Yes, specific video editing and 3D rendering software can take advantage of a combination of GPU and integrated graphics.
2. Will Using Both Gpu And Integrated Graphics Consume More Power?
Yes, using both may increase power consumption, so it’s essential to consider laptop battery life.
3. How Do I Check If My Computer Supports Using Both Gpu And Integrated Graphics?
Check your motherboard and processor specifications. Most modern motherboards and processors support hybrid graphics configurations. Additionally, refer to your system’s BIOS/UEFI settings for Multi-GPU or Hybrid Graphics options.
4. Can I Connect Multiple Monitors While Utilizing Both GPU and Integrated Graphics?
Yes, in many cases, you can connect multiple monitors when using both graphics options.
5. Are There Any Power Consumption Considerations When Using Both GPU and Integrated Graphics?
Both can increase power consumption, so monitoring temperatures and power usage is essential.
Read More: